The Present Indefinite tense is a part of grammar in English. It is the basic building block of the English language and literature. Without studying these tenses, your educational journey is incomplete. Tenses are the fundamental element in sentence making.
The Present Indefinite tense is a core element in primary school curricula. It is taught in every syllabus, whether Edexcel or Cambridge.
Whether you’re an O-level or Matric student, or even if you are an A-level or FSc student, the Present indefinite tense is a part of your syllabus.
Most students get confused between the simple present tense and the present indefinite tense. These are the same tenses with two different names. Present indefinite is the old name.
This guide will clarify your understanding of the present indefinite tense and help you prepare for your exams with a clear understanding. This article also contains a worksheet to exercise this concept.
What is the present indefinite tense?

The Present Indefinite tense is derived from the Indefinite tense. Indefinite tense is a term for a group of actions that contain simple present, simple past, and simple future tense, describing actions without specifying if they are completed or not.
The definition of the present indefinite tense refers to actions that happen regularly, facts that remain constant, or general truths. It is also used to express feelings, opinions, and scheduled events. The present indefinite tense is also known as the simple present tense. It is used to express present action/ activities, habitual action, daily activities, universal fact, or possession and state.
Examples:
- The sun rises in the east.
- She plays the piano every day.
Structure:
The structure of the Present Indefinite Tense depends on whether the subject is singular or plural. The Present Indefinite Tense follows a simple pattern, but the structure changes depending on whether the subject is singular or plural. Understanding this structure is essential because it determines how the main verb changes in a sentence.
The basic structure is:
Subject + Base Form of Verb (V1)
For plural subjects (I, we, you, they), use the base form (V1).
For singular subjects (he, she, it, or any singular noun), add s or es to the verb.
When to Add “s” or “es” to the Verb?
Use s for most verbs:
- play → plays
- read → reads
Use es for verbs ending in:
- -ss → pass → passes
- -sh → wash → washes
- -ch → teach → teaches
- -o → go → goes
- -x → fix → fixes
Verbs ending in consonant + y change y → ies:
- try → tries
- carry → carries
Verbs ending in vowel + y simply take s:
- play → plays
- enjoy → enjoys
Examples:
Plural Subjects (use V1):
- I eat breakfast at 8 AM.
- They play cricket after school.
- We study English every day.
Singular Subjects (use V1 + s/es):
- He eats breakfast at 8 AM.
- She watches cartoons every morning.
- The teacher explains the lesson clearly.
Rules:
To use the Present Indefinite Tense correctly, it is important to follow a few basic grammar rules. These rules guide how verbs change with different subjects and how auxiliaries (do/does) are used in negative and interrogative sentences. Mastering these rules helps students avoid common mistakes and form accurate sentences that express habits, routines, universal truths, and general facts.
Key Rules:
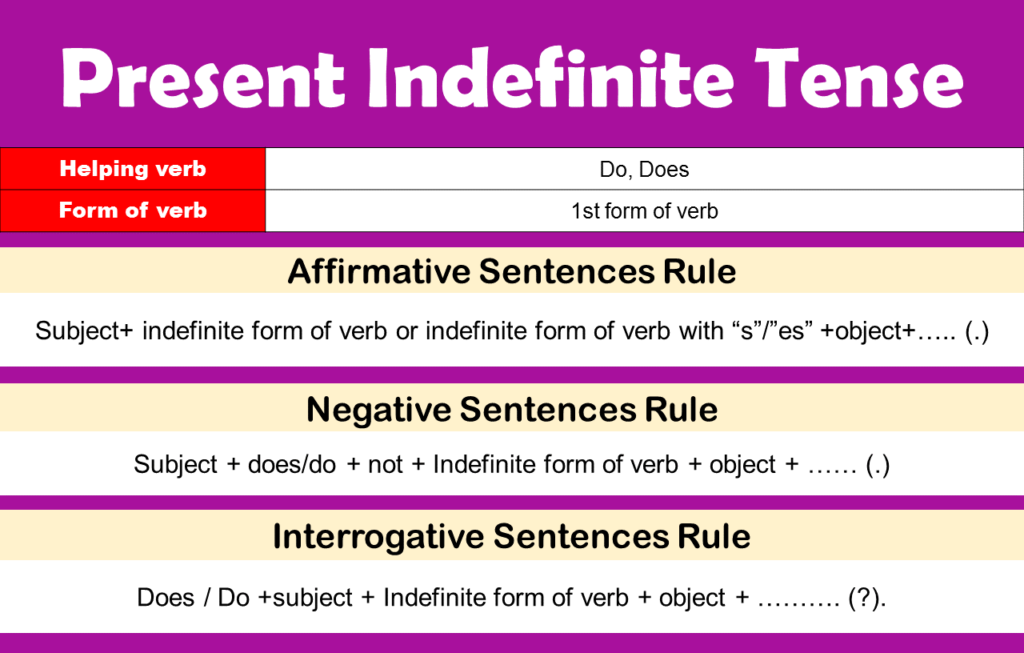
- Use V1 for plural subjects (I, we, you, they)
Example: They work hard. - Add s/es for singular subjects (he, she, it)
Example: She writes well. - Use ‘do’ with plural subjects and ‘does’ with singular subjects
Example: Does he speak English? - Do not use ‘s/es’ after ‘does’
❌ Does he speaks English?
✔ Does he speak English? - Use Present Indefinite for daily routines, universal truths, habits, and facts
Example: The sun rises in the east.
Types of Simple Present Tense:
The Simple Present Tense can be expressed in various sentence types, depending on its meaning and purpose. Two of the most commonly used forms are negative sentences and interrogative sentences. Understanding their structures helps students form correct sentences in everyday communication, exams, and writing tasks.
- Affirmative:
Affirmative are the positive sentences. They are used to express habits, daily routines, universal truths, general facts, and regular actions. These sentences state something in a simple, positive manner without using not.
The structure of affirmative sentences depends on the subject of the sentence—whether it is singular or plural.
Structure:
Subject + V1 (base form) / V1 + s/es + object
- Use V1 with: I, we, you, they
- Use V1 + s/es with: he, she, it, or singular nouns
Examples
- I wake up early.
- We play tennis every evening.
- You speak English fluently.
- They visit the library on Fridays.
- He drinks coffee every morning.
- She teaches Math.
- The dog barks at strangers.
- Negative:
Negative sentences in the Present Indefinite Tense are used to express something that does not happen, a habit someone doesn’t follow, or a fact that is not true. These sentences are formed using the auxiliaries do not (don’t) and does not (doesn’t) followed by the base form of the verb (V1).
Structure
Subject + do/does + not + V1 + object
- Use do not (don’t) with: I, we, you, they
- Use does not (doesn’t) with: he, she, it
Examples
- I do not like tea.
- She does not watch TV.
- They do not eat junk food.
- He does not drive a car.
- The bus does not stop here.
- Interrogative:
Interrogative sentences are used to ask questions in the Present Indefinite Tense. These sentences begin with do or does followed by the subject and the base form of the verb. They are commonly used in daily conversation to inquire about habits, routines, or general information.
Structure
Do/Does + subject + V1 + object + ?
- Use do for: I, we, you, they
- Use does for: he, she, it
Examples
- Do you play football?
- Does he work in a bank?
- Do they live in Karachi?
- Does she bake cakes?
- Do cats drink milk?
Active and Passive Voice of Present Indefinite Tense:
The Present Indefinite Tense can be written in both Active Voice and Passive Voice, depending on what the speaker wants to emphasize.
- In Active Voice, the focus is on the doer of the action (the subject).
- In Passive Voice, the focus shifts to the receiver of the action (the object), which becomes more important than who performed it.
Understanding both structures helps students write clearly and choose the correct form based on context, especially in formal writing, reports, and exam answers.
Active Voice Structure:
Subject + V1 / V1 + s/es + Object
Passive Voice Structure:
Object + is/am/are + V3 + by + Subject
Examples
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
| She writes a letter. | A letter is written by her. |
| They help the poor. | The poor are helped by them. |
| He cleans the room. | The room is cleaned by him. |
Present Indefinite Tense Passive Voice:
The Passive Voice of the Present Indefinite Tense is used when the focus is on the action itself rather than the person performing it. It is commonly used in formal writing, reports, announcements, and situations where the doer of the action is unknown or not important. In passive voice, the object of the active sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence, and the verb takes the form is/am/are + V3 (past participle).
Structure
Object + is/am/are + V3 + by + Subject
Examples
- The homework is done by the students.
- The gate is opened at 7 AM.
- The books are read by the children.
- The house is cleaned every day.
- English is spoken in many countries.
Present Indefinite Tense vs Present Continuous Tense
| Feature | Present Indefinite | Present Continuous |
| Describes | Habitual actions, facts | Actions happening right now |
| Example | She writes stories. | She is writing a story. |
| Structure | Subject + V1/V1+s/es | Subject + is/am/are + V1+ing |
Common Mistakes Students Make:
Even though the Present Indefinite Tense is simple, many students often make small but frequent errors, especially with verb forms, the use of do/does, and adding unnecessary endings. Identifying these mistakes is the first step toward using the tense correctly. Here are some of the most common errors and their correct forms:
- ❌ She go to school.
✔ She goes to school. - ❌ Do he plays cricket?
✔ Does he play cricket? - ❌ He do not likes coffee.
✔ He does not like coffee. - Using ing forms incorrectly
❌ I am know the answer.
✔ I know the answer. - Adding “s/es” after does
❌ Does she likes chocolate?
✔ Does she like chocolate?
Understanding these mistakes helps students become more confident and accurate when using the Present Indefinite Tense. By recognizing where errors occur, whether in verb forms, auxiliary usage, or sentence structure, learners can quickly improve their grammar. With regular practice and careful attention, these mistakes can be easily avoided.
Present Indefinite Worksheet / Practice Sentences:
VACE Global has prepared a short exercise for you to test your learning from this blog. Below is a short exercise that can help you judge what you have learned from this blog about the present indefinite tense:
Q1: Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb:
- She ___ (go) to school daily.
- They ___ (play) football every evening.
- He ___ not ___ (eat) meat.
- Do you ___ (speak) English?
- The sun ___ (rise) in the east.
- My mother ___ (cook) delicious food.
- I ___ (visit) my grandparents every Sunday.
- The train ___ (leave) at 9 PM.
- Cats ___ (like) milk.
- Does she ___ (read) novels?
Q2: Change into Negative:
- He reads a book.
- They visit the park.
- She sings well.
- The baby sleeps early.
- I trust you.
- She makes breakfast every morning.
Q3: Change into Interrogative:
- You know the answer.
- She drinks coffee.
- They watch movies.
- He writes emails daily.
- They enjoy parties.
- The dog barks loudly.
Q4: Change from Active to Passive Voice:
- She cleans the room.
- The teacher checks the papers.
- He buys a new phone.
- They open the shop at 8 AM.
- The chef cooks the meal.
- The students complete the assignment
Q5: Identify the Type (Affirmative / Negative / Interrogative):
- She does not like chocolate.
- Do they play cricket?
- He walks to school every day.
- They don’t watch TV at night.
- Does she know your name?
- Birds fly in the sky.
Q6: Spot the Error and Correct It:
- She do not goes to school.
- Does he plays football?
- They eats lunch at 2 PM.
- He do his homework daily.
- Does she likes tea?
Q7: Make Your Own Sentences
(Students demonstrate understanding by creating original examples.)
- Make 2 affirmative sentences.
- Make 2 negative sentences.
- Make 2 interrogative sentences.
Conclusion:
The Present Indefinite Tense is one of the most important building blocks of English grammar. It helps students express habits, routines, universal truths, and facts clearly and confidently. By understanding its structure, rules, formulas, and common mistakes, learners can improve both their spoken and written English with ease.
At VACE Global, our expert English teachers break down grammar concepts like the Present Indefinite Tense through real-life examples, interactive practice, and step-by-step explanations. Whether you struggle with verb forms, interrogative structures, or passive voice, our qualified instructors ensure that every concept becomes simple, clear, and fully understandable. Students not only learn the rules but also master their application through guided exercises and personalized feedback.
VACE Global also provides students with merit-based scholarships, which can take that financial burden off your shoulders and get you the best-quality tuition at an affordable price.
Ready to improve your English grammar and secure top grades?
Enroll now with VACE Global and start learning with the best online O-Level and A-Level tutors.
FAQs:
1. What is the Present Indefinite Tense?
It is a tense used to talk about habits, routines, facts, and universal truths.
2. What is the formula for the Present Indefinite Tense?
- Affirmative: Subject + V1/V1+s/es
- Negative: Subject + do/does not + V1
- Interrogative: Do/Does + subject + V1
3. When do we use “does” and “do”?
- Does → he, she, it, singular nouns
- Do → I, we, you, they
4. What is the passive voice of Present Indefinite?
Object + is/am/are + V3 + by + subject
5. Is Present Indefinite the same as Simple Present?
Yes, both terms refer to the same tense.
6. Do we use Present Indefinite for future events?
Yes, for fixed schedules:The train leaves at 7 PM.
